An orthopedic implant is a medical device used to restore function in bones and joints. These implants are made from strong materials like titanium and stainless steel. They are often used in surgeries to repair fractures or replace damaged joints.
Orthopedic implants play a crucial role in helping patients regain mobility. After an injury, patients may find it challenging to perform everyday tasks. Implants help bridge this gap, providing stability and support. However, not all implants work perfectly. Some patients experience complications or rejection of the device.
Understanding how orthopedic implants work is vital. They rely on the body's ability to integrate with foreign materials. This process can vary from person to person, leading to different recovery experiences. It's important to reflect on these outcomes as patients navigate their orthopedic journey.
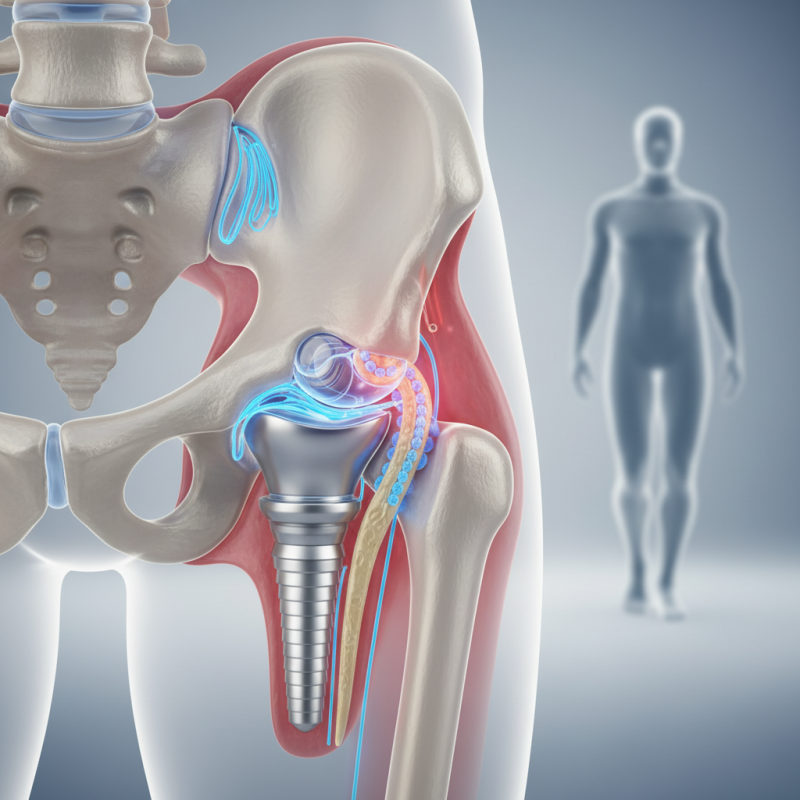
Orthopedic implants are medical devices used to replace or support damaged bone or joint structures. These implants can be made from metals, ceramics, and polymers. According to the Orthopedic Research Society, over 1.5 million orthopedic implants are used annually in the United States alone. This impressive number highlights their increasing prevalence in modern medicine.
The effectiveness of these devices can vary widely. Many people benefit from them, returning to normal activities. However, some face complications, such as infections or implant failure. Research indicates that up to 10% of patients may require additional surgery due to complications from their implants. This raises important questions about the longevity and performance of these devices.
Innovations in implant technology are ongoing and critical. Currently, many implants utilize advanced materials and coatings to enhance integration with bone. Reports show that the use of bioactive coatings can increase implant success rates significantly. Yet, challenges remain. Not every patient responds positively to these innovations. Each individual's healing process and implant compatibility varies. This underscores the need for continued research and refinement in the field of orthopedic implants.
Orthopedic implants are essential tools in modern medicine. They help repair bone fractures, replace joints, and stabilize the spine. Various types of orthopedic implants cater to different needs. Common implants include plates, screws, rods, and joint replacements. Each type serves a specific purpose, ensuring that patients can regain mobility and reduce pain.
Screws and plates are often used in fracture fixation. They hold fractured bones together, allowing them to heal properly. Rods are typically used in spinal surgeries to stabilize the spine. Joint replacements, such as hips or knees, provide a new surface for damaged joints. The choice of implant depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon's preference.
**Tips:** When considering orthopedic implants, seek multiple opinions. Not every implant is suitable for everyone. Recovery can be slow and requires patience. Always follow your doctor’s recommendations for rehabilitation. It’s easy to overlook the importance of physical therapy, yet it plays a vital role in successful recovery.
This bar chart illustrates the number of orthopedic procedures performed using various types of orthopedic implants. The data reflects thousands of procedures across different categories, providing insight into the prevalence and utility of each type of implant in clinical settings.
Orthopedic implants are devices used to support and stabilize bones and joints. They play a crucial role in medical procedures like joint replacements and bone repairs. Understanding how these implants work in the human body is essential for patients and caregivers alike.
When an orthopedic implant is inserted, it bonds with the surrounding bone. This bond can help restore functionality and alleviate pain. Over time, the body grows new bone around the implant, providing stability. However, implant success isn’t guaranteed. Some patients experience complications like infection or implant rejection. It’s vital to stay informed and maintain open communication with healthcare providers.
Tip: Pay attention to any unusual pain or discomfort after surgery. Early detection of issues can lead to better outcomes.
It’s crucial for patients to follow post-surgery guidelines. Engaging in physical therapy can enhance recovery. Yet, not everyone adheres to these recommendations, which may slow healing. Recognizing the importance of gradual progression in physical activity is essential for a successful recovery.
Tip: Keep a journal to track your recovery progress. This can help motivate you and recognize areas needing attention.
The surgical process of implanting an orthopedic device involves several crucial steps. Initially, the patient undergoes imaging studies like X-rays or MRIs. These help the surgeon assess the damaged area. Accurate planning ensures optimal placement of the implant to restore function.
During surgery, anesthesia is administered. The surgeon makes an incision near the injury site. This step is vital, as improper incision location can lead to complications. The damaged bone or joint is then prepared. In some cases, the implant may require adjustments to fit correctly. According to industry reports, around 18 million orthopedic implants were performed globally in 2021. However, complications arise in about 2% of cases, highlighting the importance of precision.
After placing the implant, the surgeon closes the incision. Sutures or staples secure the skin. Post-operative care is essential. Patients need to follow rehabilitation protocols. This aids recovery and enhances implant functionality. Tracking patient outcomes shows that around 90% report significant pain relief and improved mobility after surgery. Yet, some still experience limitations, proving that constant reflection on surgical techniques is necessary for better results.
Recovery after orthopedic implant surgery is a critical process. Patients often need physical therapy to regain strength. Studies show that up to 80% of patients see improvement in mobility within six months. However, recovery can vary widely among individuals. Factors like age and overall health play significant roles.
Proper rehabilitation starts immediately after surgery. Gradual weight-bearing can help accelerate healing. Patients report varying levels of pain during the recovery. Understanding pain management is essential. A 2020 survey indicated that nearly 40% of patients felt unprepared for postoperative discomfort.
Support systems also matter. Emotional and physical support aids recovery. Peer support groups can enhance motivation. Yet, some patients report feelings of isolation. This can slow their rehabilitation. Reflecting on social connections is important in the healing journey. Close attention to diet and nutrition can also enhance recovery outcomes. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that any complications are promptly addressed.
| Implant Type | Material | Common Uses | Recovery Time | Rehabilitation Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint Replacement | Titanium | Hip, Knee | 6-12 weeks | Physical Therapy, Aquatic Therapy |
| Fracture Fixation | Stainless Steel | Long Bones, Pelvis | 4-10 weeks | Mobilization, Strength Training |
| Spinal Fusion | Bone Graft Materials | Spine Stabilization | 3-6 months | Posture Training, Core Strengthening |
| Dental Implants | Titanium | Missing Teeth | 2-6 months | Oral Hygiene, Regular Check-ups |
